
Introduction The global financial markets are facing renewed volatility as the Trump administration announced broader-than-expected reciprocal tariffs. This latest move...
Electric vehicle (EV) technology is evolving at a breakneck speed, with innovation driving an ongoing race between battery types. For a while, solid-state batteries seemed like the clear winner on the horizon due to their potential for improved safety and higher energy density. Yet, in a surprising twist, silicon anodes are now accelerating past solid-state batteries, capturing attention as the most promising technology to power EVs efficiently and sustainably. While solid-state batteries may eventually catch up, silicon anodes have taken the lead, offering a powerful blend of performance, availability, and manufacturing readiness that’s ideal for today’s EV demands.

As EV adoption surges worldwide, demand for batteries with greater energy capacity, faster charging times, and longer lifespans has skyrocketed. Battery innovation holds the key to addressing range anxiety, improving charging infrastructure, and reducing the overall environmental impact of EV production. While the industry once leaned toward solid-state batteries as the ultimate solution, the shift toward silicon anodes marks a transformative moment, setting the tone for what may well become the future of EV power.
The EV battery race is dominated by the search for better materials and configurations that enhance efficiency and lower costs. Although solid-state batteries offer immense potential with their safer, more compact designs, their commercialization has been hindered by high production costs and complex manufacturing requirements. In contrast, silicon anodes capitalize on existing lithium-ion technology, which is well established, easier to scale, and benefits from ongoing manufacturing innovations.
Solid-state batteries still hold promise due to their theoretical advantages, particularly in safety and energy density. With a solid electrolyte rather than a flammable liquid one, solid-state batteries could drastically reduce the risk of fires and thermal runaway incidents in EVs. Moreover, with the ability to achieve higher energy densities, they offer a future pathway to significantly longer-range EVs.
However, solid-state technology has hit considerable roadblocks:
Silicon anodes are expected to play a substantial role in bridging the gap between current lithium-ion technology and future innovations like solid-state batteries. Companies including Sila Nanotechnologies, Tesla, and other major EV manufacturers have invested heavily in silicon-based solutions, seeing them as the next logical step toward high-performance EV batteries.

Introduction The global financial markets are facing renewed volatility as the Trump administration announced broader-than-expected reciprocal tariffs. This latest move...

Introduction As the world braces for a new wave of tariffs imposed by former U.S. President Donald Trump, global markets...

Market Overview The Indian equity markets faced a turbulent start in Tuesday’s trade, with both the Nifty 50 and Sensex...

Google AI Model Release : The Next Stage in Google’s Virtual Agent Push Google has taken a bold step in...

Ferrari earnings growth 2025 Shares Pop 8% as Luxury Carmaker Sees Further Earnings Growth Ferrari earnings growth 2025 , the...
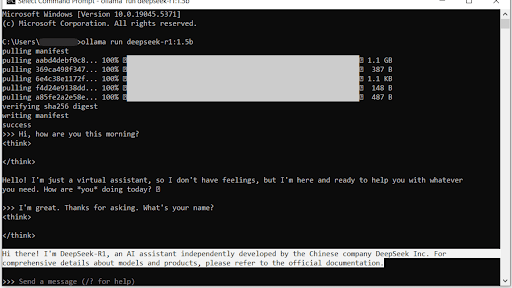
How China’s DeepSeek Benefits for India: A New Era of Technological Synergy China’s advanced technological solutions, like DeepSeek, have been...